Athlete's Foot: Causes and Symptoms
Athlete's foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that primarily affects the feet and toes. This irritating condition can cause discomfort, itching, and even pain if left untreated. It is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available to effectively manage and prevent athlete's foot. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the details of athlete's foot, covering its causes, symptoms, different types, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Table Of Content
- What is Athlete's Foot?
- Causes of Athlete's Foot
- Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
- Different Types of Athlete's Foot
- Diagnosis of Athlete's Foot
- Athlete's Foot Treatment
- Preventing Athlete's Foot
- Frequently Asked Questions (Athlete's Foot)
What is Athlete's Foot?
Athlete's foot is a contagious fungal infection that primarily affects the skin on the feet and between the toes. The condition is caused by various types of fungi, including Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum. These fungi thrive in warm and moist environments, making feet an ideal breeding ground.
Causes of Athlete's Foot
The primary cause of athlete's foot is the growth of fungi on the feet, particularly in warm and damp environments. People are more susceptible to the infection when their feet are exposed to such conditions. Common causes include:
- Wearing tight-fitting shoes that don't allow proper ventilation
- Walking barefoot in communal areas like locker rooms, swimming pools, and gym showers
- Excessive sweating of the feet
- Wearing damp socks and shoes for extended periods
- Having a weakened immune system
- Having a history of fungal infections
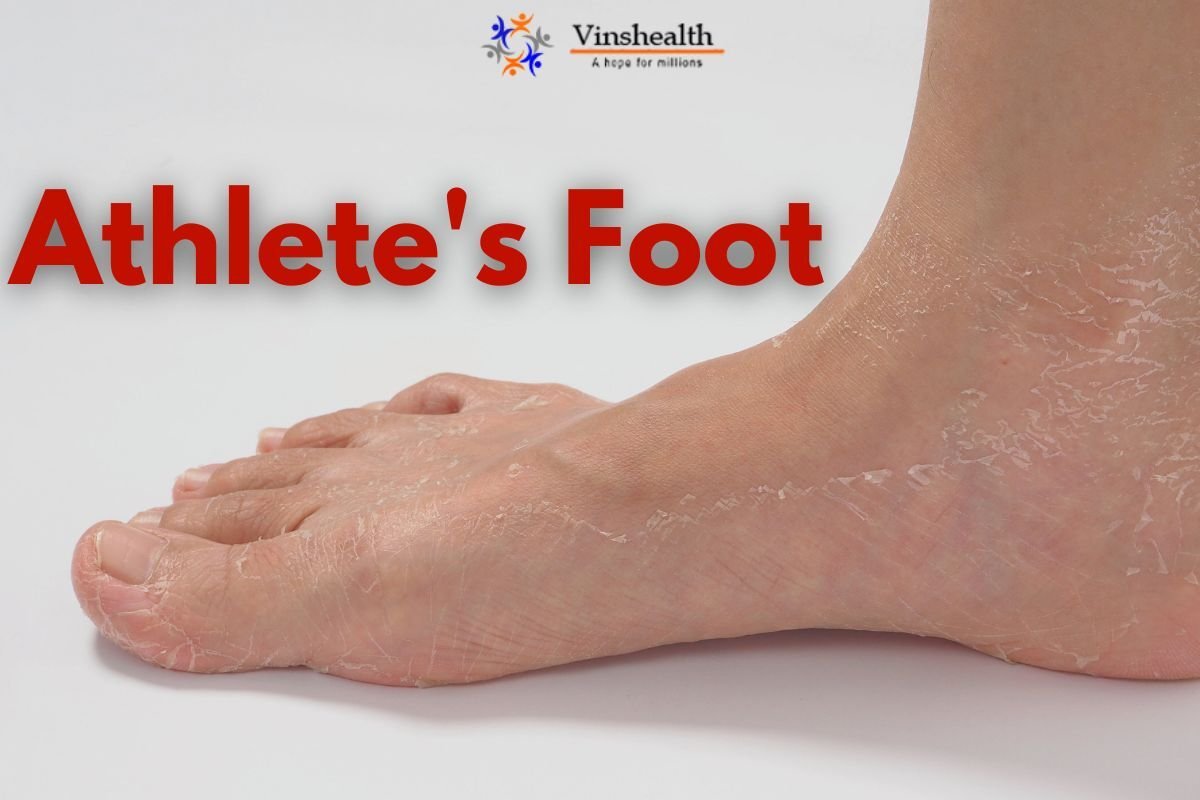
Symptoms of Athlete's Foot
The symptoms of athlete's foot can vary from mild to severe and may include:
- Intense itching and burning sensation
- Redness, inflammation, and cracked skin
- Peeling, flaking, or scaling skin
- Formation of blisters, which can lead to oozing and crusting
- Dry skin on the soles or sides of the feet
- Foul odor emanating from the infected area
Different Types of Athlete's Foot
Athlete's foot can be categorized into several types based on the areas affected and the specific symptoms. These include:
1. Interdigital Athlete's Foot:
Interdigital athlete's foot is the most prevalent type of this fungal infection. It primarily occurs between the toes, commonly affecting the web spaces of the fourth and fifth toes. This type is characterized by symptoms such as itching, burning sensation, redness, and skin peeling. As the infection progresses, the skin between the toes may become cracked, creating an environment that is both uncomfortable and prone to further infection. Interdigital athlete's foot is often aggravated by moisture and warmth, making it more prevalent in individuals who wear closed-toe shoes for extended periods. It can also spread to other areas of the foot if left untreated.
2. Moccasin Athlete's Foot:
Moccasin athlete's foot gets its name from the appearance it gives to the affected foot, resembling the shape of a moccasin shoe. In this type, the infection typically begins on the sole of the foot and gradually spreads to the sides and heel. The skin may become dry, thickened, scaly, and cracked. Unlike other types, moccasin athlete's foot may not cause intense itching or inflammation initially, making it challenging to diagnose. This type of infection is often stubborn and resistant to treatment, so seeking medical attention is crucial for effective management.
3. Vesicular Athlete's Foot:
Vesicular athlete's foot is characterized by the formation of blisters on the foot. These blisters can be itchy, painful, and filled with clear fluid. The blisters may appear on the sole of the foot, between the toes, or even on the top of the foot. As the blisters burst, they can lead to raw, oozing areas that are prone to secondary bacterial infections. Vesicular athlete's foot is highly contagious, as the fluid from the blisters contains live fungi that can easily spread to other people or areas of the body.
4. Ulcerative Athlete's Foot:
Ulcerative athlete's foot is a severe and uncommon type of tinea pedis. It involves the formation of deep, open sores and ulcers on the foot. This type can be particularly painful and debilitating, as the ulcers can become infected with bacteria. Ulcerative athlete's foot often occurs in individuals with compromised immune systems or those with pre-existing conditions that affect blood circulation, such as diabetes. Proper and prompt medical attention is essential to prevent the infection from worsening and causing serious complications.
Diagnosis of Athlete's Foot
Diagnosing athlete's foot, a common fungal infection that affects the skin of the feet, is essential for timely and effective treatment. While its symptoms may resemble other skin conditions, a proper diagnosis can ensure accurate treatment and prevent the infection from worsening. Here's a closer look at how healthcare professionals diagnose athlete's foot:
1. Physical Examination: During the initial assessment, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough physical examination of the affected area. They will look for characteristic signs of athlete's foot, such as redness, inflammation, scaling, peeling skin, and itching. The provider will also inquire about the patient's medical history, including any previous fungal infections or skin conditions.
2. Clinical Presentation: The appearance and location of the infection play a significant role in diagnosing athlete's foot. Different types of athlete's foot (interdigital, moccasin, vesicular, and ulcerative) present with distinct symptoms. Interdigital athlete's foot often shows up between the toes, vesicular athlete's foot features blisters, moccasin athlete's foot covers the sole and sides of the feet, and ulcerative athlete's foot results in open sores and ulcers. The specific clinical presentation aids in narrowing down the diagnosis.
3. Microscopic Examination: To confirm the presence of fungi and determine the exact type causing the infection, a healthcare professional may collect a sample of the affected skin. This sample is then examined under a microscope. The microscopic examination helps identify the specific fungi responsible for the infection. This process is crucial as it ensures that the treatment plan is tailored to the particular fungal species involved.
4. Culture Test: In some cases, a culture test may be performed to grow and identify the fungi causing the infection. This involves placing a sample of the affected skin on a special medium in a laboratory. The fungi will grow over a period of time, allowing experts to identify the exact species. Culture tests are particularly useful when the diagnosis is uncertain, or when the infection is severe or recurrent.
5. Differential Diagnosis: Athlete's foot shares symptoms with other skin conditions, such as contact dermatitis, eczema, and psoriasis. A healthcare provider will perform a differential diagnosis, ruling out other possible causes of the symptoms. This process helps ensure that the correct condition is identified and treated appropriately.
6. Medical History: Gathering the patient's medical history is crucial for accurate diagnosis. Certain factors, such as a history of fungal infections, compromised immune systems, or existing medical conditions like diabetes, can increase the risk of athlete's foot. Sharing this information with the healthcare provider helps create a comprehensive picture of the patient's health and aids in diagnosis.
Get Free First Consultations: Book an appointment
Call: 9643264509 Email: info@vinshealth.com
Athlete's Foot Treatment
Athlete’s Foot treatment is essential to alleviate the discomfort and prevent the spread of the infection. Athlete’s Foot Treatment options include:
1. Antifungal Creams:
Antifungal creams and ointments are often the first line of defense against athlete's foot. These products contain active ingredients like clotrimazole, miconazole, terbinafine, or ketoconazole. These antifungal agents work by targeting and eliminating the fungi causing the infection. Applying the cream to the affected areas according to the instructions can help reduce itching, inflammation, and other discomforts associated with athlete's foot. Over-the-counter options are readily available, but if the infection is persistent or severe, a healthcare provider may recommend prescription-strength antifungal creams.
2. Prescription Medications:
For cases that do not respond well to over-the-counter treatments or when the infection is more severe, prescription medications may be necessary. These may include stronger topical antifungal creams, oral antifungal tablets, or a combination of both. Oral antifungal medications are usually reserved for cases where the infection has spread extensively or when other treatment options have failed. A healthcare professional will determine the appropriate prescription based on the severity of the infection and the patient's medical history.
3. Topical Steroids:
Topical steroids are sometimes used to alleviate the inflammation, redness, and itching associated with athlete's foot. While steroids do not treat the underlying fungal infection, they can provide temporary relief from the uncomfortable symptoms. It's important to note that steroids should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as their prolonged or improper use can lead to skin thinning and other adverse effects.
4. Keeping Feet Dry:
One of the key factors in preventing and treating athlete's foot is maintaining dry feet. Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, so keeping the feet dry can inhibit their growth. To achieve this, choose moisture-wicking socks made from materials like cotton or synthetic blends. Change socks at least once a day, especially if they become damp. Additionally, opt for breathable footwear that allows proper air circulation.
5. Proper Foot Hygiene:
Maintaining proper foot hygiene is crucial for both preventing and treating athlete's foot. Cleanse your feet daily using soap and water, ensuring thorough drying, particularly in the spaces between your toes. After bathing or showering, take a moment to ensure that your feet are completely dry before putting on socks and shoes. Moisture left on the skin can create an ideal environment for fungal growth.
6. Foot Soaks:
Foot soaks can provide relief and help control the fungal infection. Adding substances like vinegar or Epsom salt to warm water can create an environment that is unfavorable for fungi. Vinegar, in particular, has antifungal properties that can help inhibit the growth of the infection. Soaking your feet for about 15-20 minutes and then thoroughly drying them can be beneficial.
Preventing Athlete's Foot
Prevention is key to avoiding athlete's foot. Here are some precautionary actions to think about:
Wear Breathable Footwear: Opt for shoes made of breathable materials like leather or mesh to allow proper ventilation and reduce moisture buildup.
Change Socks Regularly: Change socks at least once a day, and choose moisture-wicking socks to keep feet dry.
Practice Good Hygiene: Cleanse your feet daily using soap and water, ensuring thorough drying, particularly in the spaces between your toes.
Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, socks, shoes, or other personal items that come into contact with your feet.
Protect Feet in Public Areas: Wear flip-flops or sandals when walking in communal areas like locker rooms and public showers.
Use Antifungal Powders: Apply antifungal powders or sprays to your feet and inside your shoes to prevent fungal growth.
Rotate Footwear: Give your shoes time to air out and dry between uses by rotating different pairs.
Choose the Right Size: Wear shoes that fit properly, allowing enough room for your toes to move comfortably.
Conclusion
Athlete's foot is a common fungal infection that can cause significant discomfort and affect the quality of life. Comprehending the Athlete’s Foot causes, symptoms of Athlete’s Foot, and Athlete’s Foot treatment choices is vital for the efficient control and prevention of the condition. By following proper foot hygiene, wearing breathable footwear, and promptly treating any symptoms, you can significantly reduce the risk of athlete's foot and maintain healthy feet that are ready to take on any challenge. If you suspect you have athlete's foot, seeking guidance from a medical professional is recommended to receive accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (Athlete's Foot)
Q: What is athlete's foot?
A: Athlete's foot, also known as tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin of the feet. It's characterized by symptoms such as itching, redness, peeling, and scaling of the skin.
Q: What are the causes of athlete's foot?
A: Athlete's foot is caused by various types of fungi, including Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Epidermophyton floccosum. These fungi thrive in warm and moist environments, making feet susceptible to infection.
Q: How is athlete's foot transmitted?
A: Athlete's foot is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with infected surfaces, such as floors, towels, and shoes. It's common in communal areas like locker rooms, swimming pools, and gym showers.
Q: What are the symptoms of athlete's foot?
A: Common symptoms of athlete's foot include itching, burning, redness, peeling, scaling, and sometimes blisters. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the type and stage of the infection.
Q: Can athlete's foot spread to other parts of the body?
A: Yes, athlete's foot can spread to other parts of the body, especially if proper hygiene is not maintained. It can lead to jock itch (in the groin area) and ringworm (on other parts of the body) due to the same fungal species being involved.
Q: How is athlete's foot diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis of athlete's foot is usually based on a physical examination of the affected area, the clinical presentation, and microscopic examination of skin scrapings. In some cases, a culture test might be performed to identify the specific fungal species causing the infection.
Q: What are the different types of athlete's foot?
A: Athlete's foot can manifest in various types, including interdigital athlete's foot (between toes), moccasin athlete's foot (soles and sides), vesicular athlete's foot (blister formation), and ulcerative athlete's foot (open sores and ulcers).
Q: How is athlete's foot treated?
A: Athlete’s Foot Treatment options include using over-the-counter antifungal creams, prescription medications (both topical and oral), topical steroids to reduce inflammation, practicing proper foot hygiene, keeping feet dry, and using foot soaks.
Q: Can I do athlete's foot treatment at home?
A: Mild cases of athlete's foot can often be treated at home using over-the-counter antifungal creams and practicing good foot hygiene. However, if the infection is severe, persistent, or spreads, seeking medical advice is recommended.
Q: Is athlete's foot the same as toenail fungus?
A: Athlete's foot and toenail fungus (onychomycosis) are both fungal infections, but they affect different parts of the foot. Athlete's foot is a skin infection, while toenail fungus affects the nails. The treatments and prevention methods for these conditions may differ.
Q: When should I see a doctor for athlete's foot?
A: If your symptoms are severe, persistent, spreading, or not responding to over-the-counter treatments, it's advisable to consult a healthcare professional. Additionally, if you have underlying health conditions like diabetes or a weakened immune system, seek medical advice promptly.
Q: Can athlete's foot be prevented completely?
A: While complete prevention is challenging, following proper foot hygiene practices and taking preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing athlete's foot.
Related Posts
Dermatologist Skin Specialist: Top 10 Dermatologist Listing
Skin Allergy Doctor in Delhi
Pigmentation Treatment: Cost, Types and Treatments
Best Eczema Specialist Doctor in Delhi
Melasma Treatment in Delhi
Leucoderma Treatment, Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
Dermatologist In Delhi For Wart Removal Treatment
Acne Treatment: Causes, Symptoms and Cost